Bacteria Basics
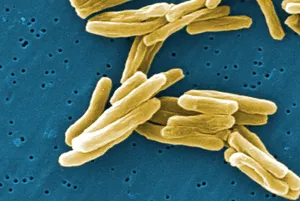
Image 1: Electron Microscope Image of a bacilli bacteria
Definition
Bacterium (Plural: bacteria) is a single-cell prokaryotic organism that lives in clusters and survives in specific conditions. Let's examine its key features.
Yes, you are right! The main difference between archaea and bacteria is the presence of a peptidoglycan cell wall. Archaea DO NOT have a peptidoglycan cell wall.
Key Features
These are the key features that a bacterium has:
- Each bacterium consists of one single cell only
- Bacteria are prokaryotic cells, which means there is no nuclear membrane.
- Bacteria cell walls are made of peptidoglycan
- Bacteria reproduce asexually by binary fission (more on that in another chapter)
- Bacteria do not have membrane-bound organelles, like mitochondria and smooth endoplasmic reticulums.
Types
There are a lot of different types of bacteria. They can be classified into different shapes:
- Cocci: Sphere-shaped bacteria
- Bacilli: Rod-shaped bacteria
- Spirilla: Spiral-shaped bacteria
- Vibrio: Kidney-shaped bacteria
- Others: A lot of other different shapes
Functions
Bacteria can be harmful or beneficial. Harmful bacteria are called pathogens. Let us take a look at some of the functions of beneficial mesophile bacteria.
Decomposition
Decomposition is a process where dead organisms are broken down into smaller organic matter. Bacteria and fungi act as decomposers in this case.
Bacteria break down these organisms using enzymes. These enzymes attach to organic matter and break it down into smaller and different organic matter. Plants and trees can reuse this broken-down organic matter! For example, proteins are broken down into amino acids, and carbohydrates are broken down into sugar (Byjus, n.d.).

Image 2: Fermented Beer (Science, 2017)
Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that turns sugar into acid, gases, and alcohol without oxygen. It is used in food production, such as cheese, alcohol, and yogurt, because it enhances flavors by leaving the food in a controlled environment.
Cheese is so flavourful thanks to a bacteria called lactococcus lactis, which ferments lactose (milk sugar) into lactic acid. This gives the cheese a nutty flavor that we all love (well, at least I love it).
Alcohol is also very flavourful (I haven't had it before) because it is made by fermentation. Alcohol, such as wine, vodka, and beer, is fermented using glucose, maltose, and fructose from different vegetation, such as grapes, potatoes, and wheat.
Digestive System
There are about 100 trillion bacteria in our digestive system, which are known as our gut microbiome. These bacteria have both good and bad actions (Harvard, 2023).
The entire gut microbiome empire has a close relationship with us. It helps us break down food, absorb nutrients, and maintain our gut health while we (as a host) provide shelter and nutrients for them.
Interestingly, your microbiome is one of the stakeholders in deciding what meal you will have for lunch. Different bacteria send different signals to your brain, requesting a specific food intake.
For example, a veggie-loving bacteria will request the brain to eat veggies. If you do not eat veggies, these bacteria will die. When you eat excess fast food, fast food-loving bacteria will thrive and crave for more fast food. , everyone knows this equation.
If you keep your guts healthy, you will be healthy.
Ecological balance
We need bacteria to help us break down food and survive, and the bacteria need us in order to survive. The same goes for other animals and plants.
Ecological balance!
Novato Bacteria
The Novato bacteria is a mesophilic pathogenic bacteria, which means it causes harm to humanity.
Project Novato was established to eradicate the bacterium. However, it is not just us, we need you, we need everyone, we need humanity to save humanity.
Let us take a deep dive into topics regarding the Novato Bacteria.